The GMAT Exam is a critical step for candidates aiming to secure admission into top business schools worldwide. Designed to evaluate analytical reasoning, problem-solving, and data interpretation skills, the GMAT assesses your ability to excel in a rigorous MBA program.
A clear understanding of the GMAT syllabus is essential for effective preparation. It helps you:
- Identify key topics covered in the GMAT Exam Syllabus, ensuring you focus on the most important concepts.
- Plan a structured study approach to maximize efficiency and boost your score.
- Avoid surprises on test day by familiarizing yourself with the question types and format.
This article provides a detailed breakdown of the GMAT Syllabus 2025, starting with a high-level overview of the three main sections—Quantitative, Verbal, and Data Insights. We also take a deep dive into the specific topics tested in each section, difficulty level and strategies—complete with sample questions for practical insight equipping you with the knowledge you need to create a focused and effective GMAT study plan.
The best way to understand the GMAT Syllabus & exam format is by trying the test out for yourself. Try Free GMAT Mock now.
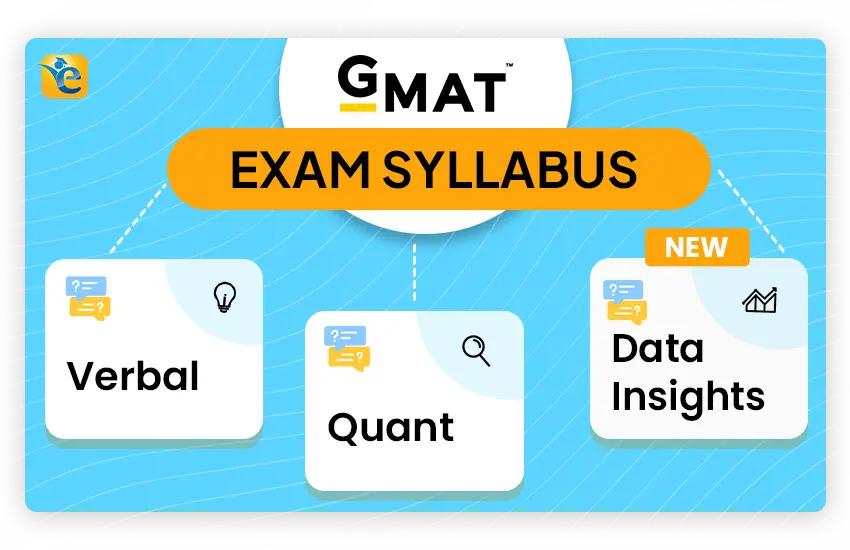
What is the GMAT Syllabus?
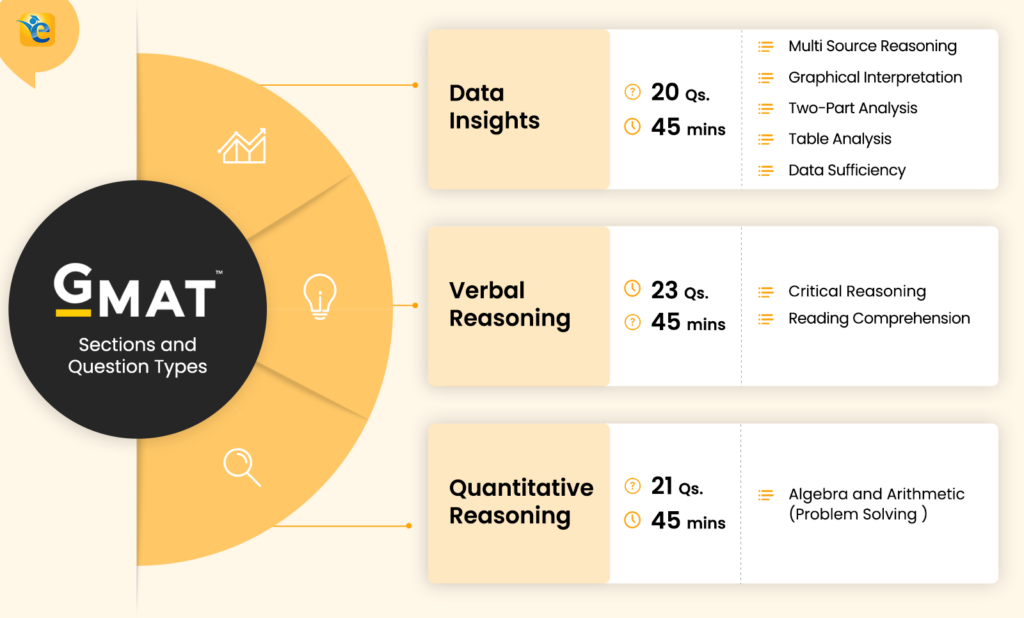
The GMAT Syllabus includes three main sections: Verbal Reasoning , Quantitative Reasoning and Data Insights , with 45-minute duration for each section. Below is high level GMAT Syllabus (also called the GMAT exam pattern):
| Section | Number of Questions | Time Allocated |
| Quantitative Reasoning | 21 | 45 minutes |
| Verbal Reasoning | 23 | 45 minutes |
| Data Insights | 20 | 45 minutes |
| Total | 64 | 2 hours 15 minutes (plus an optional 10-minute break) |
GMAT Syllabus 2025: Topics Tested on the GMAT
The table below provides a breakdown of the key topics tested in each GMAT section:
| GMAT Section | GMAT Syllabus |
| Quantitative Reasoning | Algebra Arithmetic |
| Verbal Reasoning | Reading Comprehension : Main idea + Supporting idea + Inference + Application + Logical structure + Style Critical Reasoning : Strengthen + Weaken + Flawed + Supports + Damages |
| Data Insights | Data Sufficiency Multi-source Reasoning = Examination or analyses of data from various sources (text, tables, graphics, or combination of these) + recognition of discrepancy + inference + determination of the relevance of data Table Analysis Graphics Interpretation = Interpretation of information from graphics (scatter plot, x/y graph, bar chart, pie chart, or statistical curve distribution) + finding relationship + inference Two-part Analysis = Quant, Verbal, or a combination of both + evaluating trade-offs + solving simultaneous equations + finding relationships |
Let’s dive into the detailed GMAT syllabus to guide your preparation effectively.
Create your Personalized Study Plan for the GMAT. And reach your target score in the shortest possible time.
GMAT Syllabus: Section wise Detailed Look
The GMAT exam is divided into three main sections and is completed within a total duration of 2 hours and 15 minutes. These sections are:
- Verbal Reasoning
- Quantitative Aptitude Section
- Data Insights
Q: Can I choose my own section order on the GMAT ?
Yup! You can do the three sections (Quantitative Reasoning, Verbal Reasoning, and Data Insights) in any order you’d like.
Further, we will break down the syllabus for each part, highlight the skills being tested, and provide sample questions to give you a practical insight into the exam format.
GMAT Verbal Syllabus (Verbal Reasoning Section)
The Verbal Reasoning section assesses the test taker’s ability to read, comprehend written passages, and evaluate arguments.
“In the Verbal Reasoning section, test takers have 45 minutes to answer 23 questions.“
The questions within this section are primarily of two types:
- Critical Reasoning
- Reading Comprehension.
Critical Reasoning (CR)
Critical Reasoning questions evaluate your capability to construct and analyze arguments and develop or assess action plans. Based on short passages, usually under 100 words, these questions ask you to choose an answer that either strengthens, weakens, or evaluates an argument. No specialized topic knowledge is needed.
Skills Tested in GMAT CR
The skills pertaining to reasoning that are tested by the GMAT Critical Reasoning are divided into four categories – Analysis, Construction, Critique, and Plan.
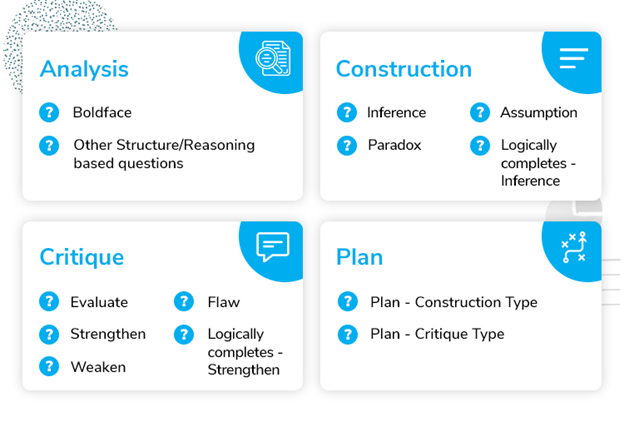
1) Analysis
Here, we need to analyse an argument. This involves understanding the logical reasoning/structure of the argument and the relationships between various parts of the argument.
2) Construction
Here, we are tested on our ability to construct solid arguments. For example – finding what can be logically concluded/inferred or finding what new information would be needed for the argument to hold true.
3) Critique
Here, we are tested on our ability to question the validity of arguments, identify how to strengthen or weaken arguments, identify the flaw in an argument, etc. In other words, we are critiquing a given argument.
4) Plan
Plan questions test our ability to construct and critique arguments pertaining to a plan of action. For example – a question may ask us to find the flaw in a plan, or maybe the underlying assumption for a plan to work. Plan questions, from a conceptual standpoint, are either construction questions or critique questions.
How to Build these Skills?
Here is the Solution! – Our course is structured to build your skills in a logical Sequence and in the shortest possible time. Try it now!
Sample Questions : CR
Below are some sample questions for testing different skills, click on slider to see more questions:
Check this article on GMAT CR for the solution.
For a detailed understanding of each CR question type, skills and sample practice questions, read our article “GMAT Critical Reasoning – What it tests and how to build these skills.
Reading Comprehension (RC)
Reading Comprehension questions assess your ability to interpret the text, understand the logical connections between key points, draw inferences, and comprehend the evolution of quantitative ideas.
Mainly the test focuses on the following reading skills: identifying the main and supporting ideas, drawing inferences, applying information, understanding logical structure, and analyzing style.
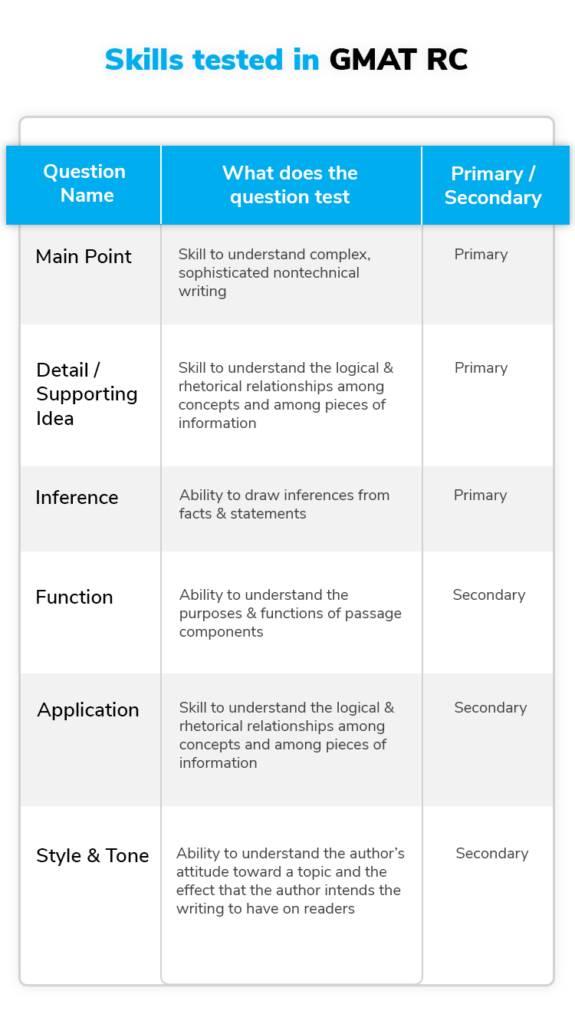
Skills tested in GMAT RC
Skills measured in GMAT Reading Comprehension are tested through certain question types. We can divide these question types into the following broad and sub-categories:
- Primary question types
- Main point
- Detail/Supporting idea
- Inference
- Secondary question types
- Function
- Application
- Style and Tone
Here are the skills tested through each of these question types:
How to Build these Skills?
Here is the Solution to building RC Skills! – Our course is structured to build your skills in a logical Sequence and in the shortest possible time. Try it now! And our New personalized study planner is designed to help you reach your target score in the shortest possible time.”
Sample Question – RC
GMAT Reading Comprehension Practice Question – Main Point
There are two theories that have been used to explain ancient and modern tragedy. Neither quite explains the complexity of the tragic process or the tragic hero, but each explains important elements of tragedy, and, because their conclusions are contradictory, they represent extreme views.
The first theory states that all tragedy exhibits the workings of external fate. Of course, the overwhelming majority of tragedies do leave us with a sense of the supremacy of impersonal power and of the limitation of human effort. But this theory of tragedy is an oversimplification, primarily because it confuses the tragic condition with the tragic process: the theory does not acknowledge that fate, in a tragedy, normally becomes external to the hero only after the tragic process has been set in motion. Fate, as conceived in ancient Greek tragedy, is the internal balancing condition of life. It appears as external only after it has been violated, just as justice is an internal quality of an honest person, but the external antagonist of the criminal. Secondarily, this theory of tragedy does not distinguish tragedy from irony. Irony does not need an exceptional central figure: as a rule, the more ignoble the hero the sharper the irony, when irony alone is the objective. It is heroism that creates the splendor and exhilaration that is unique to tragedy. The tragic hero normally has an extraordinary, often a nearly divine, destiny almost within grasp, and the glory of that original destiny never quite fades out of the tragedy.
The second theory of tragedy states that the act that sets the tragic process in motion must be primarily a violation of moral law, whether human or divine; in short, that the tragic hero must have a flaw that has an essential connection with sin. Again it is true that the great majority of tragic heroes do possess hubris, or a proud and passionate mind that seems to make the hero’s downfall morally explicable. But such hubris is only the precipitating agent of catastrophe, just as in comedy the cause of the happy ending is usually some act of humility, often performed by a noble character who is meanly disguised.
The primary purpose of the passage is to:
A. compare and criticize two theories of tragedy
B. develop a new theory of tragedy
C. summarize the thematic content of tragedy
D. reject one theory of tragedy and offer another theory in its place
E. distinguish between tragedy and irony
If you would like to try attempting some RC questions to get a feel for RC, check out our free trial now.
For a detailed understanding of each RC question type, skills and sample practice questions, read our article “ GMAT Reading Comprehension – What it tests” and “Tips to improve GMAT RC“.
GMAT Quant Syllabus (Quantitative Reasoning Section)
The Quant section of the GMAT evaluates your understanding of algebra and arithmetic fundamentals and your ability to apply this knowledge in problem-solving scenarios.
“In the Quantitative Reasoning section, test takers have 45 minutes to answer 21 Problem-solving questions”.
Here is the GMAT Quant syllabus (Problem Solving Questions):
| Arithmetic | Algebra |
| Multiples and Factors | Monomials, polynomials |
| Number Properties | Functions |
| Fractions | Exponents |
| Decimals | Quadratic equations |
| Percentage | Inequalities and basic statistics |
| Power and Roots | Algebraic expressions and equations |
| Average | Permutation and combination |
| Probability | Progressions |
| Set Theory | |
| Mixtures and allegations | |
| Ratio and proportion | |
| Descriptive Statistics | |
| Pipes, cisterns, and work time | |
| Speed, time, distance | |
| Simple and Compounded Interest |
Achieving a high Quant score requires a solid grasp of concepts and their application to solving questions. Here are some tips for scoring high in the GMAT Quant Section.
You’ve seen the syllabus. Now let’s make it personal.
These topics look different for everyone—based on your target score, starting point, and timeline. Get a personalized breakdown showing exactly which sections need the most focus and how long YOUR preparation will take.
How Long Do You Need
to Score 705?
Get a personalized study timeline
Based on your current level and target score
Know which section to prioritize
Quant, Verbal, or DI — see where to focus first
Define your target percentiles
Clear metrics for each section to hit your goal
Remember, the GMAT isn’t about memorizing formulas; it’s about understanding concepts and applying them. While it’s necessary to remember certain formulas, understanding why they work and when to use them is more important. Make sure to spend enough time with each concept to fully grasp it before moving on to the next.
We recommend studying Quant and Verbal before Data Insights as Data Insights questions require using math and verbal concepts.
Syllabus of GMAT Data Insights Section
The Data Insights section is not an adjunct; it is an integral part of the exam. The inclusion of this section in GMAT reflects the increasing importance of data literacy and analytics in the business world. This section has equal weightage in the total GMAT score.
The Data Insights section of the GMAT exam focuses on evaluating a test taker’s ability to analyze complex data and draw meaningful insights. This section assesses skills in data analysis, verbal reasoning, and math, which are essential for making informed decisions in a business management context.
“In the Data Insights section, test takers have 45 minutes to answer 20 questions. An on-screen calculator is available for this section.“
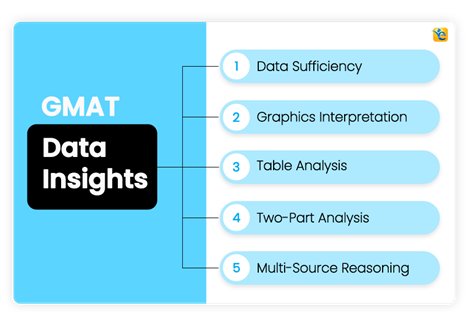
GMAT Data Insights syllabus encompasses five types of questions:
Data Sufficiency
Data Sufficiency questions assess the ability to determine whether the given data is sufficient to solve a particular problem. Test takers must evaluate the information provided and decide if it is enough to arrive at a definitive answer.
We recommend you to read below articles on Data Sufficiency:
Graphics Interpretation
Test takers are presented with graphical representations such as charts or graphs. They must analyze and interpret the data visualizations to answer questions about trends, patterns, or relationships depicted in the graphics.
Table Analysis
Test takers need to interpret and analyze data presented in tables in this question type. The questions may involve sorting data, identifying trends, or making comparisons based on the information provided.
We recommend you to read below articles:
Two-Part Analysis
This question type requires test takers to solve problems that involve multiple steps or considerations. It assesses the ability to analyze a situation, apply relevant concepts, and arrive at the correct answer by considering various factors.
Multi-Source Reasoning
This question type requires test takers to analyze information from multiple sources, including graphic, numeric, and textual data. It assesses the ability to identify relationships among various pieces of information and draw conclusions based on them.
Skills Tested in Data insights
The GMAT Data Insights section tests a variety of skills:
1. Data Interpretation and Analysis: It tests your ability to understand, interpret, and analyze complex information from varied sources.
2. Information Synthesis: This skill assesses your capability to combine different data points to create a comprehensive picture and determine the best problem-solving strategy.
3. Analytical Reasoning: Analytical reasoning examines your ability to scrutinize information and arguments and draw logical conclusions from data.
4. Quantitative Reasoning: Despite the lack of complex calculations, quantitative reasoning is key, particularly for understanding and applying quantitative aspects of data.
5. Critical Thinking: This is assessed through questions that require you to evaluate arguments or claims based on the presented data, testing your ability to critically assess information and make sound judgments.
6. Decision Making: This skill is tested through the application of all the above skills to make informed decisions or choices within a complex, data-rich context.
7. Comprehension: This skill is critical for combining textual and visual data effectively.
These skills are crucial not only for the GMAT but also in fields where data interpretation and analysis play key roles.
Prepare for the GMAT with the best GMAT Focus Mocks . We have provided a clear and concise comparison of GMAT Mocks and explained the mocks algorithm.

GMAT Syllabus 2025
The GMAT syllabus is divided into three key sections: Verbal Reasoning, Quantitative Reasoning, and Data Insights. Below is a high-level summary of the topics covered in each section:
| GMAT Verbal | GMAT Quantitative | GMAT Data Insights |
| Assumptions | Fractions | Data Sufficiency |
| Inference | Decimals | Multi-source Reasoning |
| Evaluate | Number Properties | Graphics Interpretation |
| Bold Face | Percentage | Two-Part Analysis |
| Paradox | Power and Roots | |
| Strengthen and weaken | Average | |
| Main Point | Probability | |
| Detail/Supporting idea | Set Theory | |
| Inference (RC) | Multiples and Factors | |
| Style and Tone | Mixtures and allegations | |
| Function | Ratio and proportion | |
| Application | Descriptive Statistics | |
| Pipes, cisterns, and work time | ||
| Speed, time, distance | ||
| Simple and Compounded Interest | ||
| Monomials, polynomials | ||
| Functions | ||
| Exponents | ||
| Quadratic equations | ||
| Inequalities and basic statistics | ||
| Algebraic expressions and equations | ||
| Permutation and combination | ||
| Progressions |
GMAT Verbal Reasoning
This section evaluates critical reasoning, reading comprehension, and logical analysis skills through various question types, including:
- Critical Reasoning: Assumptions, Inference, Evaluate, Bold Face, Paradox, Strengthen & Weaken
- Reading Comprehension: Main Point, Detail/Supporting Idea, Inference, Style & Tone, Function, Application
GMAT Quantitative Reasoning
This section assesses problem-solving and mathematical reasoning skills, covering:
- Number Properties: Fractions, Decimals, Power & Roots, Multiples & Factors
- Arithmetic & Algebra: Percentages, Ratios, Averages, Exponents, Quadratic Equations, Inequalities, Functions
- Applied Math: Probability, Set Theory, Mixtures & Allegations, Speed-Time-Distance, Work-Time, Interest Calculations
- Advanced Concepts: Descriptive Statistics, Permutations & Combinations, Progressions
GMAT Data Insights
This section tests the ability to analyze and interpret data in various formats, including:
- Data Sufficiency: Evaluating whether given data is sufficient to answer a question
- Multi-Source Reasoning: Analyzing information from multiple sources (text, tables, graphs)
- Graphics Interpretation: Understanding and drawing conclusions from charts, graphs, and diagrams
- Two-Part Analysis: Solving problems requiring simultaneous analysis of two variables
By mastering these topics, you can create a targeted study plan and approach the GMAT 2025 with confidence.
How to study for GMAT
According to GMAC, the new GMAT aims to assess better “higher-order critical reasoning and data literacy” skills crucial for tomorrow’s business world. But what does that mean in practical terms?
Developing a structured study plan is key. Start by familiarizing yourself with the updated GMAT syllabus, then create a personalized schedule that allocates dedicated time to each section—Quantitative, Verbal, and Data Insights. Utilize quality resources like official guides, free mock tests, and sample questions to practice regularly. Focus on identifying and improving your weak areas while reinforcing your strengths, and consistently review your progress to refine your test strategy.
We recommend you to check out our in-depth article on the GMAT Study Plan for a detailed understanding of how you should structure your GMAT preparation.
GMAT Preparation Materials
Official GMAT prep resources, including the Official Guide for GMAT (Official Guide 2023) and full-length practice tests, became available on mba.com on June 6, 2023. In addition, every e-GMATer can access an industry-leading GMAT Course with 1000+ questions and free mock test , and it will help you understand the GMAT syllabus better through practice.
Read this article to understand about the GMAT Official Prep content – What is it & How to use it.
GMAT prep resources offered by e-GMAT:
Here is the overview of the GMAT prep material offered by e-GMAT:
- Comprehensive GMAT Materials: We’ve updated our courses with GMAT Edition content, allowing existing students to access these new resources without extra costs, ensuring continuity in quality education and support.
- Data Insights (Scholaranium) : In our continuous effort to provide you with unparalleled preparation material, DI Scholaranium brings to you a whopping 350 questions, each meticulously crafted and paired with solutions, dedicated to data insights. This is in addition to the existing 500 questions available in the DI course, summing up to a total of 850 original questions.
- GMAT Mocks : We at e-GMAT are immensely proud to announce a groundbreaking advancement in GMAT preparation with the launch of our GMAT Edition mocks., developed from extensive research and simulations, these mocks promise to deliver a test experience that closely mirrors the actual exam.
- Personalized Study Planner : We have created the data-driven Personalized Study Planner for the GMAT Edition, offering customized study schedules, performance forecasts, and trackable goals to effectively navigate the updated exam demands.
Final Thoughts: GMAT Syllabus
Navigating the GMAT may initially seem daunting, but understanding its syllabus and content is the first step to mastering the exam. This article has provided a comprehensive overview of the GMAT Edition syllabus, highlighting key changes in question types and sections.
With the right preparation materials and a solid study plan, achieving a competitive score is entirely within reach. We have outlined valuable resources.
To delve deeper into your preparation strategy, we highly recommend our in-depth GMAT Study Plan article. With the right preparation, you’re not just getting ready for an exam; you’re setting the stage for a successful business career. Good luck on your GMAT journey!
Ready to tackle the GMAT Edition? e-GMAT offers a Personalized Study Planner and top-notch Free GFE mock exam to help you prepare effectively. As the most reviewed GMAT prep company on GMAT Club with 2600+ reviews we’re here to support your GFE journey. Take advantage of our free trial with the best quality content. Start your path to success today!
FAQs – GMAT Syllabus
There are Four key changes in the Focus Edition Syllabus:
1) It replaces the Integrated Reasoning section with Data Insights, which now accounts for a third of the exam and contributes equally to the total score.
2) Sentence Correction questions are removed from the Verbal section.
3) Geometry questions are removed from the Quant section.
4) The Analytical Writing Assessment (essay) is eliminated.
GMAT will test you on three sections :
1) Verbal – 45 Minutes to solve 23 questions
2) Quant – 45 Minutes to solve 21 questions
3) Data Insights – 45 minutes to solve 20 questions
The time duration of the GMAT edition is 2 hours 15 minutes.
You CANNOT skip any of the GMAT sections. A section is complete only if you answer every question, or you run out of time for that section.
Firstly, breaks are optional. If you don’t want a break, you can skip it and move on to the next section. In case you want a break, you can take one optional 10-minute break between any two sections.