Introduction
A 90th percentile or higher in the Verbal section of the GMAT Focus Edition, in other words a V84+, is attainable regardless of your initial proficiency. Take inspiration from success stories like Divy Gulati, who soared from the 18th to the 91st percentile, Antoine who improved from the 26th to the 98th percentile, and Samarth Gudwala, who climbed from the 51st to 98th percentile. These examples illustrate that with the right intensity of effort and sufficient duration of preparation, anyone can reach their target score. It is crucial to consistently track your progress and adjust your strategies as needed. In this article, we will guide you through a detailed, step-by-step approach to master the GMAT Focus Verbal Section, setting you on the path to achieving your desired score.

Video Guide : GMAT Verbal Prep
GMAT Verbal Preparation : Major Steps
Step 1: Understand your Starting Point
The first step towards mastering the Verbal section of the GMAT Focus Edition is to accurately assess your starting ability at both the sectional and sub-sectional levels. Knowing your initial percentile score is crucial as it:
- helps determine the amount of time required to reach your target score,
- identifies the key areas where you need to focus your efforts, and
- aids in planning effective study milestones.
Starting your preparation without this understanding could lead to misdirected effort and wasted energy. To obtain a clear baseline of your abilities, consider taking a Sigma-X mock test from e-GMAT.
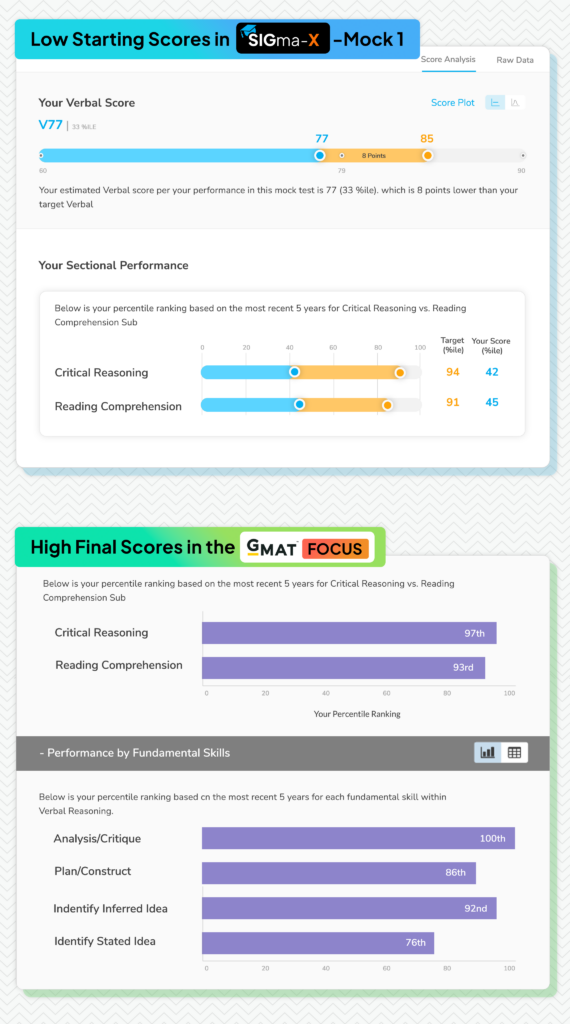
Figure 1: From Low Starting Scores in SigmaX-Mock 1, to High Final Scores in the GMAT Focus
We offer our first mock for free. Or you can opt for one of the first two, free, official GMAT mock tests. This initial assessment will be your roadmap, guiding where and how to invest your preparation time most effectively. Hence, it is important that your assessment be genuine and reliable.
Step 2: Allocate Enough Time
The second critical step in your GMAT Verbal preparation is to allocate enough time realistically. One common pitfall is setting overly ambitious timelines for improvement. For instance, while some may manage to substantially improve their verbal skills in just three weeks, others might need five or six weeks to achieve similar results. Understanding the duration of time needed based on your starting ability is essential.
| Starting Ability | Approx. Prep. Time | Utilization of Study Time |
| ~ 30th Percentile Ability | 100 hours | 60 hours: Learning Concepts and Building Skills 40 hours: Mastering Application |
| ~50th Percentile Ability | 75 to 80 hours | 40 hours: Learning Concepts and Building Skills 40 hours: Mastering Application |
| ~70th Percentile Ability | 35 to 40 hours | 30 hours: Mastering Application 10 hours: Learning or Reinforcing Concepts & Skills |
| ~85th Percentile Ability | 10 to 15 hours | Correcting Behavioral Mistakes and Building Mental Stamina and Agility |
For example, if you start at the 30th percentile, you are likely to need around a hundred hours of dedicated effort, with sixty of those hours focused on building foundational skills. Conversely, if you begin at the 70th percentile, you might reach your target score with approximately 35 to 40 hours of study, allocating 70% of this time to refining your test-taking strategies and 30% to learning and reinforcing concepts.
Clearly, your starting point not only influences the total amount of time required but also dictates how you should best utilize that time, making this understanding absolutely paramount in planning your study schedule effectively.
Step 3: Focus on Building Skills
The third step in enhancing your performance in the GMAT Verbal section is a focused effort on skill-building, a crucial aspect regardless of your starting ability. For those beginning with lower proficiency, it’s beneficial to concentrate on developing one skill at a time to ensure thorough understanding and mastery. Here are some key skills to work upon when you’re preparing for the Verbal Section of the GMAT Focus Edition:
- Comprehension: This foundational skill involves enhancing your ability to read and comprehend texts correctly. It begins with learning to grasp the meanings of key words and phrases, such as “some”, “all”, “none”, “few”, “many”, “most”, etc. An effective strategy is to visualize content while reading. We then gradually progress to understanding the building blocks of sentences, such as phrases, clauses and sentences, employing a technique called “Strategic Pausing”. At e-GMAT, we cover some of these essential techniques in our “Master Comprehension” course.
Figure 3: Partial Snapshot of Antoine’s Master Comprehension Course
Master Comprehension paves the way to a better understanding of passages, questions stems, and datasets in the Verbal, Quant and Data Insights sections.
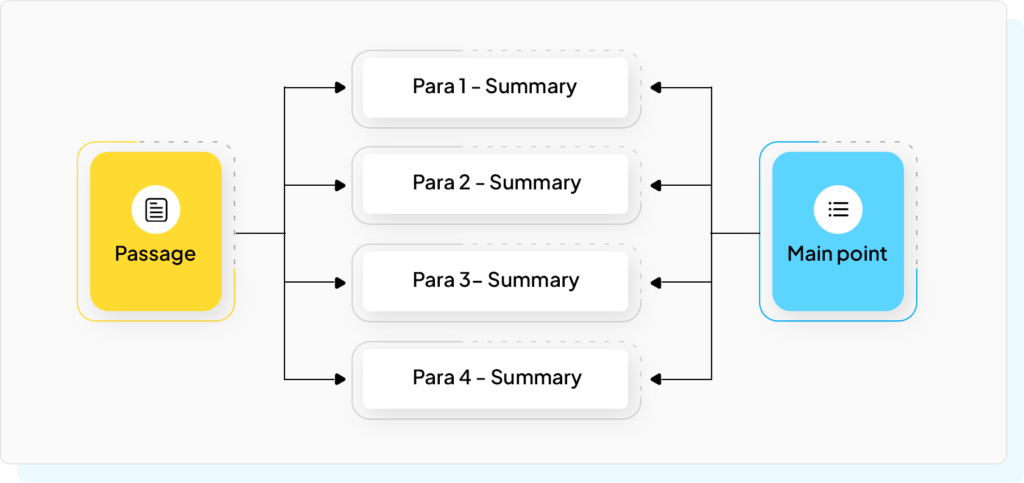
Figure 4: Snapshot from our Reading Comprehension Course: Identifying the Main Point
Finally, we begin to connect ideas across multiple statements and learn to comprehend arguments and passages, till we arrive at the main point of long passages. We learn to identify the logical structure of communication. This skill is vital as it lays the groundwork for advanced understanding and analysis.
- Drawing Inferences: Developing the ability to draw inferences involves understanding the author’s precise intent behind the text. This skill moves beyond mere comprehension, requiring you to interpret implications and meanings that are not explicitly stated but are suggested or required by the context.
Figure 5: Snapshot of Antoine’s Inference Module in our CR Course
The GMAT makes it a point to test our ability to process text and arrive at precise interpretations. This often entails looking at a statement from multiple angles. This also frequently involves making minor changes or distortions to the statement and then checking to see whether that variation can be inferred.
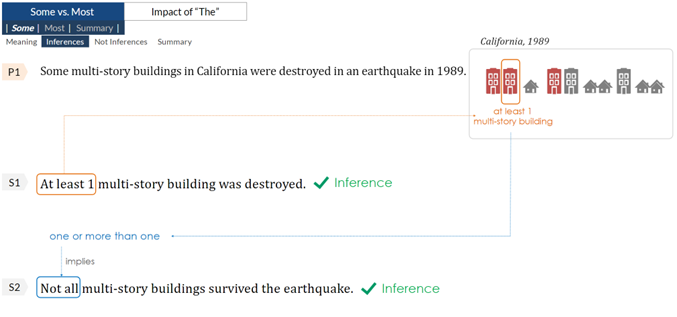
Figure 6: Snapshot of Our Lesson on the Inferences drawn from the word “Some”
Such a holistic understanding of words and sentences equips us to face not only the rigor of B-School life but also the challenges of professional life later ahead.
- Pre-thinking Assumptions: The most fundamental aspect of Critical Reasoning is the ability to identify the assumptions in a person’s argument. This rudimentary skill enables us to tackle higher order problems such as identifying weakening/strengthening statements, identifying the flaws in arguments, evaluating the strength of an argument, and so on. Hence, you should be adept at this fundamental skill. You should be able to identify assumptions in arguments even without the benefit of multiple answer choices. Only then can you truly boast of possessing Critical Thinking skills.
That’s where “Pre-thinking” comes in. Pre-thinking involves anticipating the assumptions that underlie arguments or statements before evaluating answer choices.
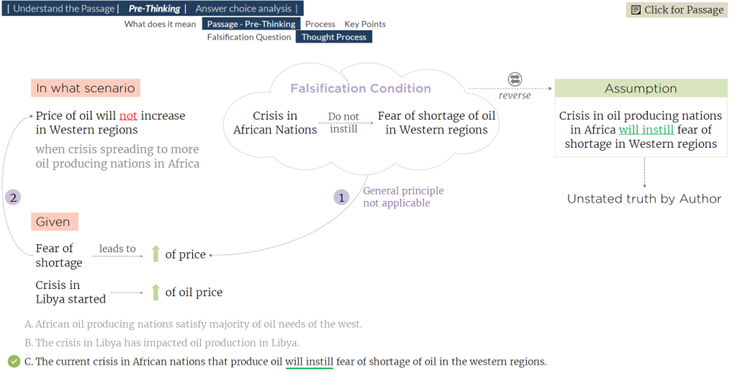
Figure 7: The Pre-thinking Process for Identifying Assumptions
This proactive approach helps in effectively tackling critical reasoning questions (in CR, RC, or Data Insights) by preparing you to quickly evaluate the validity of an answer choice and eliminate the invalid choices with ease.
“e-GMAT taught me how to pre-think, which was to understand the passage, have some idea before going into the options, and then eliminate the wrong options. Elimination becomes easy as it is easy to spot something out of scope or irrelevant.” – Samarth
Building these skills sequentially allows for a structured approach to mastering the Verbal section, ensuring that each layer of ability is solid before moving on to the next. This methodical enhancement of skills ensures a deep and effective understanding, crucial for achieving a high score in Verbal. You can experience these lessons for free in e-GMAT’s unlimited Free Trial.
Step 4: Track Your Improvement
The next step of preparing for the GMAT Verbal section is rigorous tracking of your improvement. For those starting at the 30th percentile, it is crucial not to wait until after a hundred hours of study to measure progress. The e-GMAT platform provides tools that allow you to monitor your progress in increments as small as every 30 minutes, offering personalized feedback that can guide your study plan in real-time.
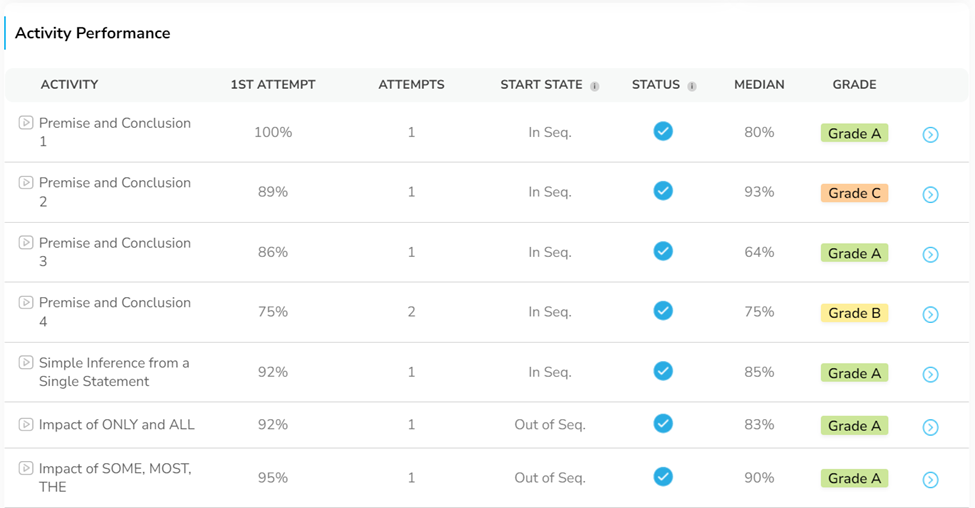
Figure 8: Antoine’s CR Activity Performance -He scored in the top 15% and scored Grade “A”s in several learning activities.
From the outset, you’re assigned grades on learning activities which serve as immediate feedback on your understanding. Furthermore, knowing early whether you need to revisit certain topics can make your study process three times more efficient. This real-time revision ensures that you solidify your understanding incrementally, which is crucial for long-term retention and skill mastery.
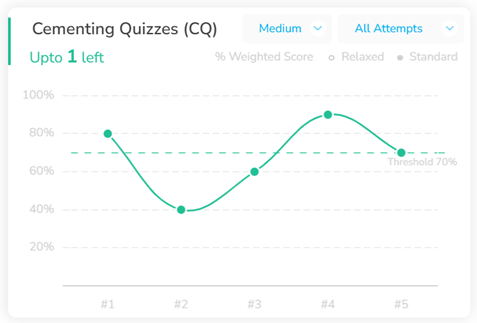
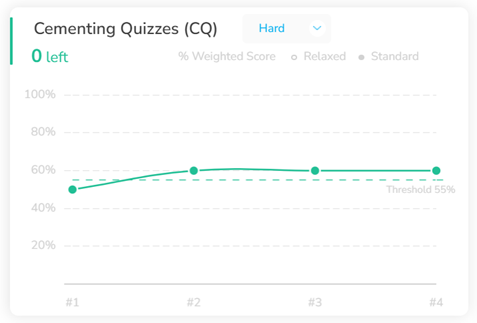
Figure 9: Antoine’s CR Cementing Journey – Medium Cementing (left) and Hard Cementing (right)
As you advance to stage two, “Cementing,” you practice applying your skills through medium and hard quizzes in a timed environment, ensuring you meet specific performance thresholds. For example, to reach the 90th percentile, you need to achieve at least 90% accuracy in medium-difficulty quizzes and 70% in hard quizzes. You should aim to first reach and maintain a 70% accuracy rate, then, during the final stages of your prep, work up to 80%, and eventually strive for 85%. This structured approach to tracking not only measures your progress but also aligns your preparation efforts with your target score, making your study time more effective and targeted.
Step 5: Build a Useful Error Log
An error log is not just a tool, but a crucial part of advancing from an average score range, such as the 60th percentile, to an excellent one, like the 90th percentile or higher. It provides invaluable insights into both behavioral and conceptual mistakes, detailing not only what errors you’re making…
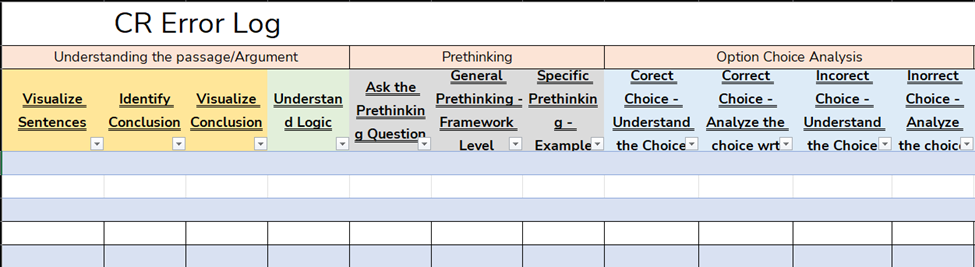
Figure 10:CR Error Log – Faltering Point Analysis
… but also when and under what conditions these errors occur, and crucially, how they can be corrected.
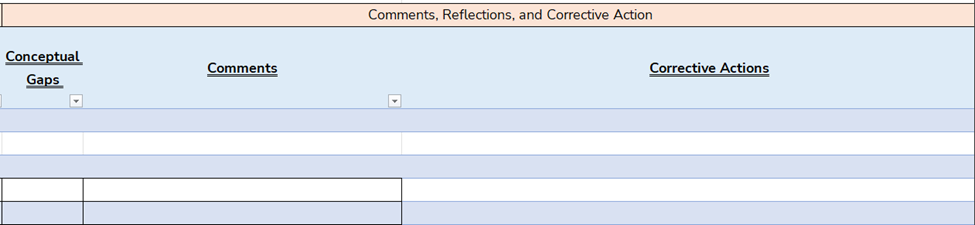
Figure 11:CR Error Log (contd.) – Conceptual Gaps & Corrective Actions
By maintaining a meticulous error log, you can pinpoint patterns in your mistakes, such as consistent errors in certain difficulty levels, specific complexities in answer choices, or particular issues with certain CR (Critical Reasoning) and RC (Reading Comprehension) passages. This targeted analysis allows you to isolate your most common errors and focus your efforts on rectifying them, making your study time more efficient and effective.
For example, while working one-on-one with students like Samarth, we provide tailored feedback and focused correction strategies that significantly improve both speed and accuracy by directly addressing the identified weaknesses . This personalized approach, facilitated by a detailed error log, ensures that preparation is not just about covering material but about refining skills and strategies in a way that specifically enhances your performance. Moreover, the Error log serves as the perfect tool for revision toward the end of your preparation.
Step 6: Follow Best Practices
Always remember to adhere to best practices that have proven effective for achieving high scores. Following these guidelines will not only enhance your learning but will also ensure your efforts are maximized.
Consistency is Key: It’s crucial to maintain a regular study schedule. Aim for at least one to one and a half hours of focused study each day. Consistency in your preparation ensures steady progress and helps ingrain the skills you are learning. Take breaks at logical intervals—such as after completing a section or before starting a new one—to keep your mind fresh and ready to absorb new information.
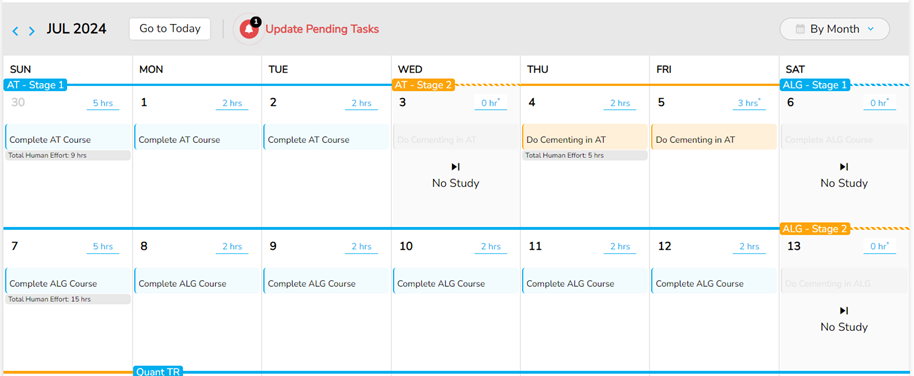
Figure 12: Execution Tracker (Calendar View) – Strategic Placement of Breaks between Learning Tasks
Application of Learning: Always focus on applying what you learn. The theoretical knowledge of concepts is useful, but the real improvement comes from applying these concepts in practice questions and mock tests and transforming them into genuine skill. This approach helps cement your learning and improve your test-taking ability.
Avoid Reliance on Tricks: While certain test-taking shortcuts and tricks may seem helpful, they can often be unreliable and lead to mistakes. For example, strategies like assuming ‘extreme’ answer choices are always incorrect, or reading only the first and last lines of a passage, can backfire. Such tricks might save time initially but can compromise your understanding and interpretation of the material, leading to lower accuracy. Instead, focus on building robust reading and reasoning skills that are widely applicable across all types of questions and passages.
By following these best practices, you’ll build a strong foundation in the necessary skills and strategies, which is the most reliable path to achieving an excellent score on the GMAT Verbal section.
Conclusion
In conclusion, reaching the 90th percentile in the GMAT Verbal section is a feasible goal for anyone willing to dedicate themselves to following established best practices. Success stories like Divy, Antoine, and Samarth exemplify that with the right approach and consistent effort, significant improvement is not only possible but can also be an enjoyable journey. The key is to understand the challenges you face and to execute your preparation plan meticulously. By embracing a systematic approach to study, focusing on building fundamental skills, tracking progress, and refining techniques, you can transform your test preparation into a rewarding process that leads to high performance. Remember, success in the GMAT Verbal section is within reach—make sure to prepare thoroughly, maintain consistency, and apply what you learn.
FAQs related to “How to prepare for GMAT Verbal”
1. Understand what the GMAT tests
2. Understand your Strengths and Weaknesses
3. Build your Study Plan
4. Master one sub-section at a time
2. How to start GMAT Verbal preparation?
Here’s the answer to one of the most commonly asked question by GMAT aspirants “How to start GMAT Verbal Prep”:
1. Understand your Strengths and Weaknesses
2. Build your Study Plan
3. Master one sub-section at a time using the following methodology:
Stage 1: Learning Concepts and Methodologies
This is the phase wherein we learn all the concepts in a sub-section and learn the process of solving the questions in that sub-section.
Stage 2: Cementing
In this phase, we cement our learnings by first solving medium difficulty questions and then hard questions. We start with relaxed timing and then progress to standard timing. Standard timing is the speed at which you’ll be expected to take the actual GMAT.
Stage 3: Test Readiness
This is the final phase of your prep. This is where you write full-length mocks to determine whether you’re ready for the GMAT or need to work on cementing your individual skills further.
Mastering one sub-section at a time entails completing the first two stages for a particular sub-section before moving to the next.
3. What are the Best Practices for GMAT Verbal Prep?
In every endeavor, there are risks. And that’s where experience comes in handy. Here is a list of a few dos and don’ts!
1. Build Core Skills | Don’t blindly practice questions
2. Estimate your starting abilities
3. Focus on One subsection at a time
4. Build an Error Log
5. Be Consistent!
How to prepare for GMAT Verbal












