OG 2020: Question No. 325
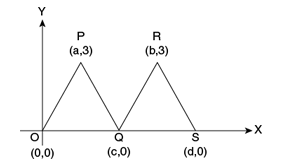
In the figure above, the vertices of ΔOPQ and ΔQRS have coordinates as indicated. Do ΔOPQ and ΔQRS have equal areas?
- b = 2a
- d = 2c
| Source | OG 2020 |
| Type | Data Sufficiency |
| Topic | Geometry |
| Sub-Topic | Triangles / Coordinate Geometry |
| Difficulty | Medium |
Solution
Steps 1 & 2: Understand Question and Draw Inferences
In this question, we are given
- A diagram, comprising of ΔOPQ and ΔQRS, along with the coordinates of their vertices, as shown.
We need to determine
- Whether ΔOPQ and ΔQRS have equal areas or not.
We know the area of a triangle is given by ½ * base * height.
- Area of ΔOPQ = ½ * OQ * height = ½ * c * 3 = 3c/2
- Area of ΔQRS = ½ * QS * height = ½ * (d – c) * 3 = 3(d-c)/2
Now, if the triangles have equal area, then
- 3c/2 = 3(d-c)/2
Or, c = d – c
Or, d = 2c
Hence, we can say that if we know whether d = 2c, we can term the statement sufficient.
With this understanding, let us now analyse the individual statements.
Step 3: Analyse Statement 1
As per the information given in statement 1, b = 2a.
- However, from this statement, we cannot say whether d = 2c or not.
Hence, statement 1 is not sufficient to answer the question.
Step 4: Analyse Statement 2
As per the information given in statement 2, d = 2c.
- Since d = 2c, we can conclude that the areas of both triangles are equal.
Hence, statement 2 is sufficient to answer the question.
Step 5: Combine Both Statements Together (If Needed)
Since we can determine the answer from statement 2 individually, this step is not required.
Hence, the correct answer choice is option B.
If you are planning to take the GMAT, we can help you with a personalized study plan and give you access to quality online content to prepare. Write to us at acethegmat@e-gmat.com. We are the most reviewed GMAT prep company on gmatclub with more than 2400 reviews and are the only prep company that has delivered more than 700+ scores than any other GMAT club partner. Why don’t you take a free trial and judge for yourself?










