Ever wondered why some GMAT test-takers breeze through Reading Comprehension passages while others struggle? The secret often lies in their ability to spot and understand keywords – particularly those indicating cause-and-effect relationships. Think of these keywords as signposts guiding you through the passage’s logical flow. Whether you’re tracking an author’s argument, understanding historical developments, or following scientific processes, mastering cause-effect keywords can transform your RC performance from uncertain to confident. In this guide, we’ll explore how these crucial keywords work and how you can use them to boost your GMAT RC accuracy.
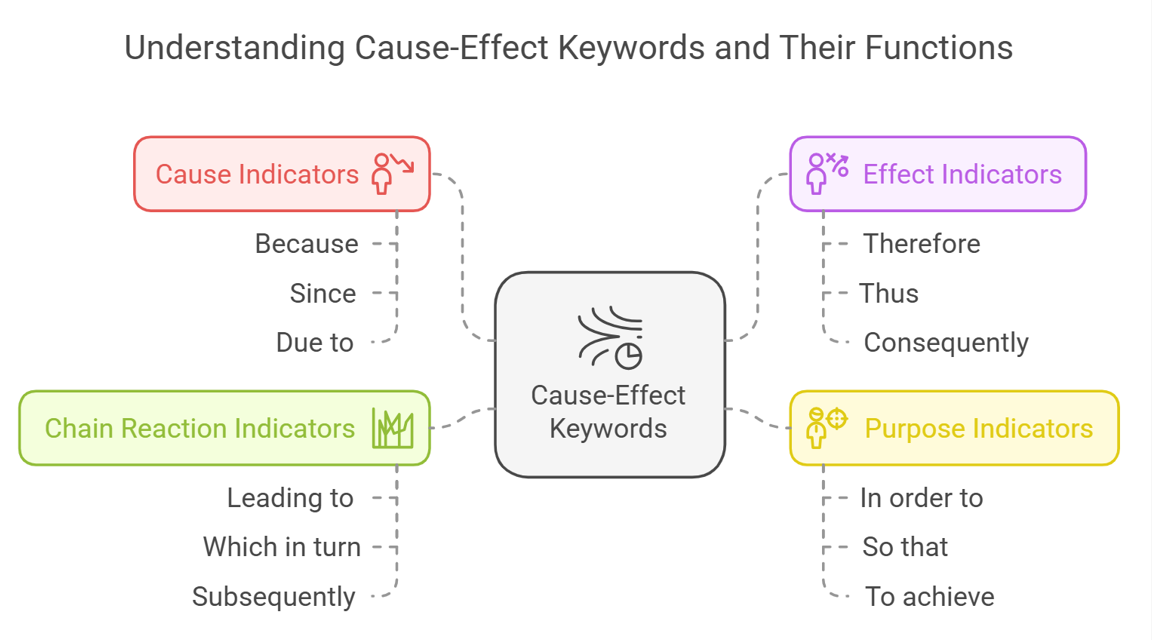
Cause-Effect Keywords
Cause-effect keywords are like detective tools – they help you uncover relationships between events, actions, and outcomes in the passage. These keywords are crucial for understanding logical connections and making valid inferences.
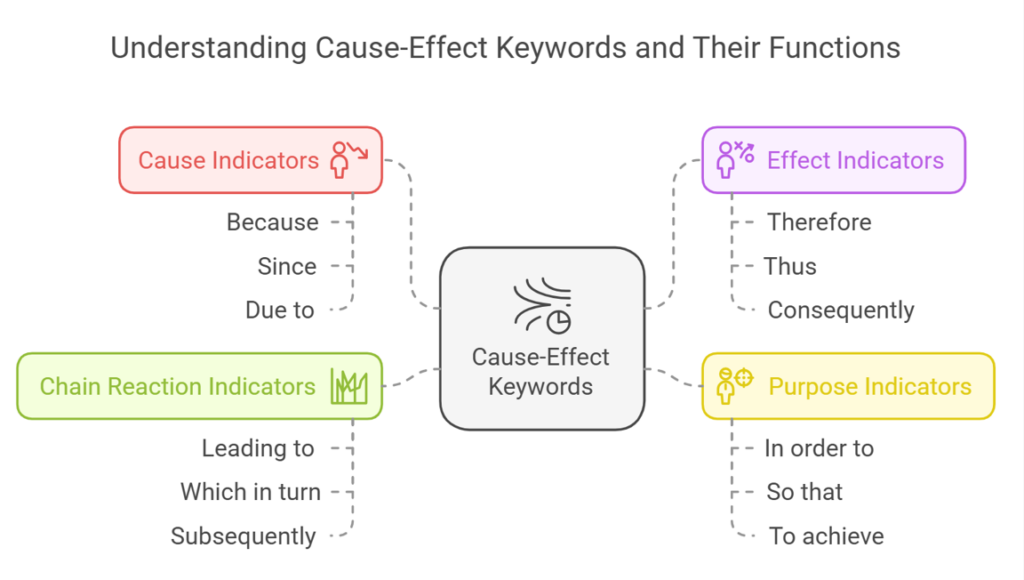
Types of Cause-Effect Keywords
Cause Indicators
- Signal why something happened
- Examples: “Because,” “Since,” “Due to,” “As a result of,” “Given that”
- Function: Introduce the reason or catalyst for an outcome
- Usage note: Often explain motivations or triggers for important events
Effect Indicators
- Signal outcomes or consequences
- Examples: “Therefore,” “Thus,” “Consequently,” “As a result,” “Hence”
- Function: Show what happened because of a previous action or condition
- Usage note: Often introduce significant conclusions or findings
Purpose Indicators
- Signal intended effects or goals
- Examples: “In order to,” “So that,” “To achieve,” “For the purpose of”
- Function: Show deliberate connections between actions and desired outcomes
- Usage note: Help understand motivations and objectives
Chain Reaction Indicators
- Signal multiple connected effects
- Examples: “Leading to,” “Which in turn,” “Subsequently,” “Eventually”
- Function: Show how effects become causes for other effects
- Usage note: Often reveal complex relationships in processes or events
Are you planning to pursue MBA at top business schools? Let us help you conquer the first step of the process i.e., taking the GMAT. Take a free mock test to understand your baseline score and start your GMAT prep with our free trial. We are the most reviewed online GMAT Prep company with 2800+ reviews on GMATClub.
How to Use Cause-Effect Keywords Effectively
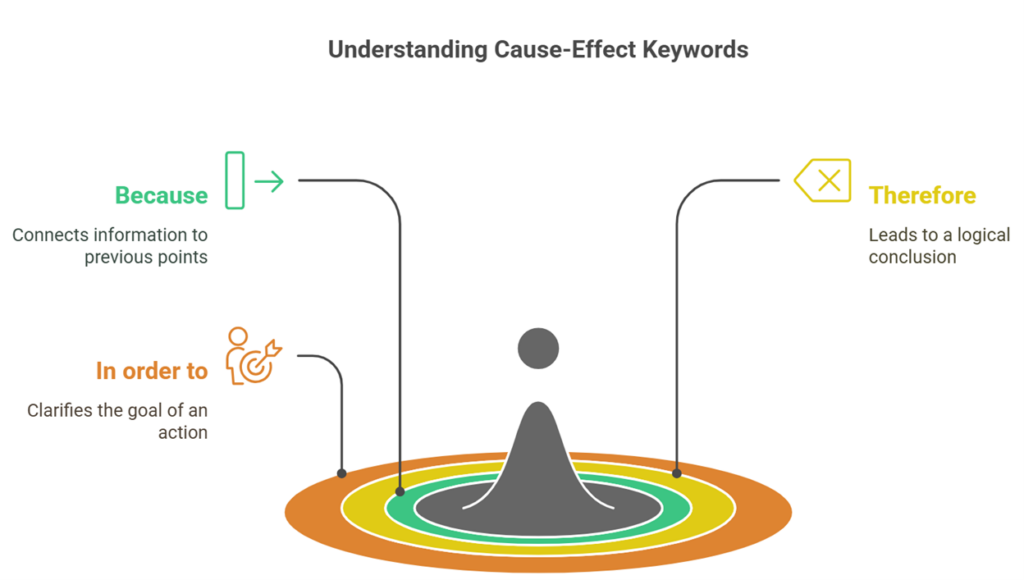
Mapping Relationships
- When you see “Because,” connect the following information to previous points
- At “Therefore,” expect a logical conclusion based on previous evidence
- With “In order to,” understand the goal driving an action
Understanding Logic Chains
- Use these keywords to follow complex argument structures
- Track how one event or condition leads to another
- Identify the author’s logical reasoning pattern
Practice Example
Consider this passage excerpt:
Because atmospheric carbon dioxide levels have increased dramatically, global temperatures have risen steadily over the past century. This warming has led to polar ice melting, which in turn has caused sea levels to rise. Consequently, coastal communities face increased flooding risks. Therefore, many cities are implementing climate adaptation strategies in order to protect vulnerable populations.
Cause-effect keywords tell us:
- “Because” → CO2 increase is the cause of temperature rise
- “led to” → Temperature rise caused ice melting
- “which in turn” → Shows chain reaction from melting to sea level rise
- “Consequently” → Shows flooding as result of previous changes
- “Therefore” → Shows logical response to threats
- “in order to” → Shows purpose of adaptation strategies
Are you planning to pursue MBA at top business schools? Let us help you conquer the first step of the process i.e., taking the GMAT. Take a free mock test to understand your baseline score and start your GMAT prep with our free trial. We are the most reviewed online GMAT Prep company with 2800+ reviews on GMATClub.
Conclusion
Mastering cause-and-effect keywords is not just about memorizing words, but understanding their strategic role in decoding complex passages. These linguistic signposts transform reading comprehension from a guessing game to a systematic approach. By recognizing and tracing causal relationships, GMAT test-takers can quickly unravel an author’s logical progression, improve inference skills, and ultimately enhance their overall RC performance. Practice and attentive reading are key to internalizing these crucial keywords.